Epi
505 – ActivEpi Lesson 2 Outline
How to Obtain Data
· Interview (Face to face, telephone, mail, e-mail, …)
· Review existing records (medical records, work records, …)
· Laboratory
· Examination (physical, CAT scan, ultrasonography …)
Select Appropriate Study Design (Lesson 3)
· Clinical Trial
· Cohort
· Case-Control
· Cross-Sectional
· Other
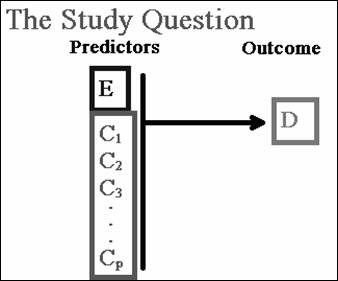
In class example: relationship between
Diet -> Breast cancer
Age
Smoking
Obesity
Physical activity
Measuring the Variables - Decisions needed on exact definitions. For example
· Illness in Sydney beach study – self report vs. physician dx?
· Define “swimming”
· Define “water quality”
Measures of Disease Frequency (Lesson 4)
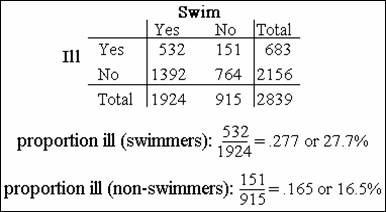
Risk of disease in exposed: R(E)
Risk of disease in nonexposed: R(not E)
Risk Ratio
Consider potential biases/flaws (Lessons 7-11):
· Study design
· Selection of participants (selection bias)
· Information collected from/on participants (information bias)
· Confounding
Methods of data analysis
Biases and flaws may lead to incorrect conclusions
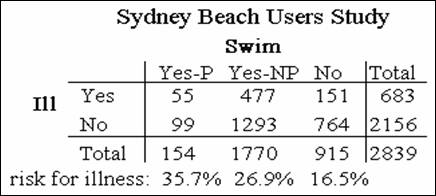
Yes-P = swam in polluted water
Yes-NP = swan in non-polluted water
No = did not swim
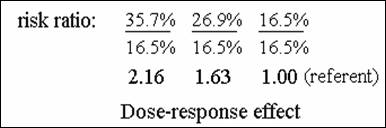
Test for trend (Lesson 14)
Examples of Epidemiologic Studies
Alcohol
consumption and breast cancer in the Nurses Health Study
Example of cohort study
Identify group of disease-free subjects
Collect exposure information
Follow over time
Results: alcohol associated with breast cancer with dose response effect
Bogalusa
Outbreak
Legionnaires disease in Bogalusa
Example of case-control study
Result: associated with misting machine for vegetables at a grocery store
The
Rotterdam Study of Alzheimer’s Disease
Cohort study of 8000 elderly
Assessed relation of smoking to Alzheimer’s accounting for age, gender, education, and alcohol consumption.
Result: smoking associated with increased risk of Alzheimer’s