LESSON 5
![]()
MEASURES OF
EFFECT
Present measures of association/effect/impact
first and then study designs?
Epi Kept Simple (Epi Info, SAS, SPSS)
Table 8.3. HIV
Infection and Intravenous Drug Use (IVDU) in Women entering New York State
Prison System.
|
|
Disease |
|
|
|
Exposure |
HIV+ |
HIV- |
|
|
IVDU + |
61 |
75 |
136 |
|
IVDU - |
27 |
312 |
339 |
|
|
88 |
387 |
475 |
ActivEpi
|
|
Exposure |
|
|
|
Disease |
IVDU+ |
IVDU- |
|
|
HIV + |
61 |
27 |
88 |
|
HIV - |
75 |
312 |
387 |
|
|
136 |
339 |
475 |
All Exams will present tables as shown in
ActivEpi
The Odds Ratio
Example
of case-control study – Haiti – diarrheal disease
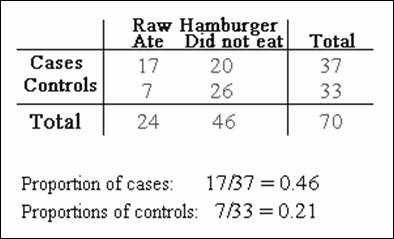
Case-control
study - Cannot compute risks, risk ratio. Can
compute the odds ratio.
Estimated
odds ratio:
ratio of the odds of exposure for cases divided by the odds of exposure for
controls. Example:
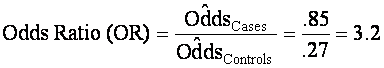
Interpretation
of odds ratio?
The
odds of exposure for cases was about 3.2 times the odds of
exposure for controls.
Calculating the Odds Ratio
Alternative
odds formula:
Odds
of exposure in cases = a/b
Odds
of exposure in controls = c/d
Odds
ratio = (a/b) / (c/d) = ad/bc (cross product ratio)
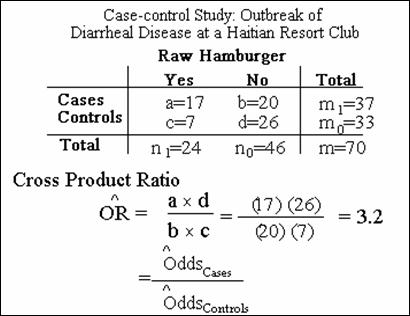
|
OR |
RR |
|
|
Case-Control Studies |
√ |
No |
|
Follow-up Studies |
√ |
√ |
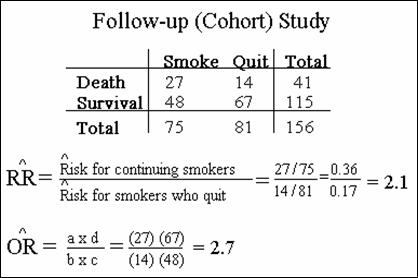
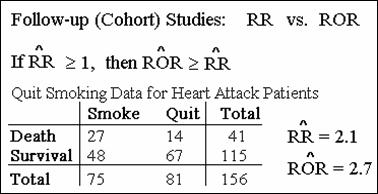
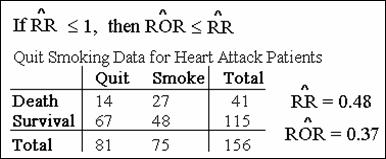
Comparing the Risk Ratio and the Odds Ratio
![]()
![]()
Note: except when RR=1, the ROR
is always further away from the null than the RR
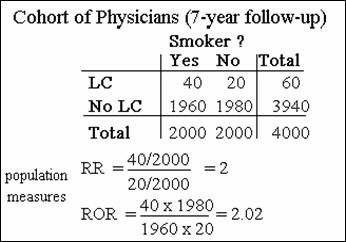
If a disease is "rare", then the risk odds ratio will closely
approximate the risk ratio.
Comparison of RR with ROR when disease infrequent
5-4 The Rate Ratio and its Characteristics
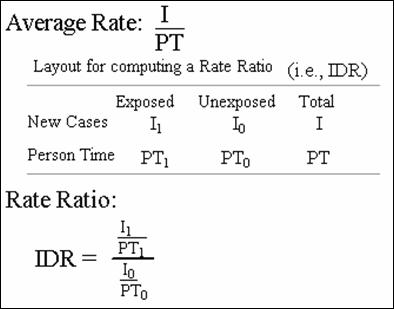
The Rate Ratio
A rate ratio is a ratio of two average
rates. It is sometimes called an incidence density ratio or a hazard
ratio.
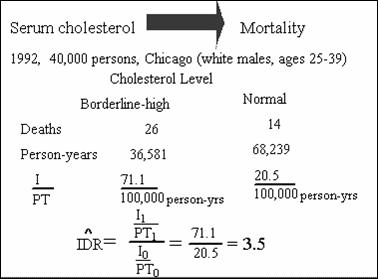
Odds
Ratio Approximation to Rate Ratio
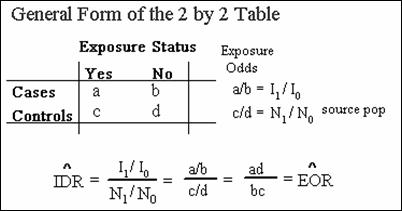
vUnder steady state
conditions, OR from case-control study approximates IDR from comparable cohort
study. (Steady-state means no major shift in the demographic make-up of source
population.)
vThis approximation does not
require the rare disease assumption.